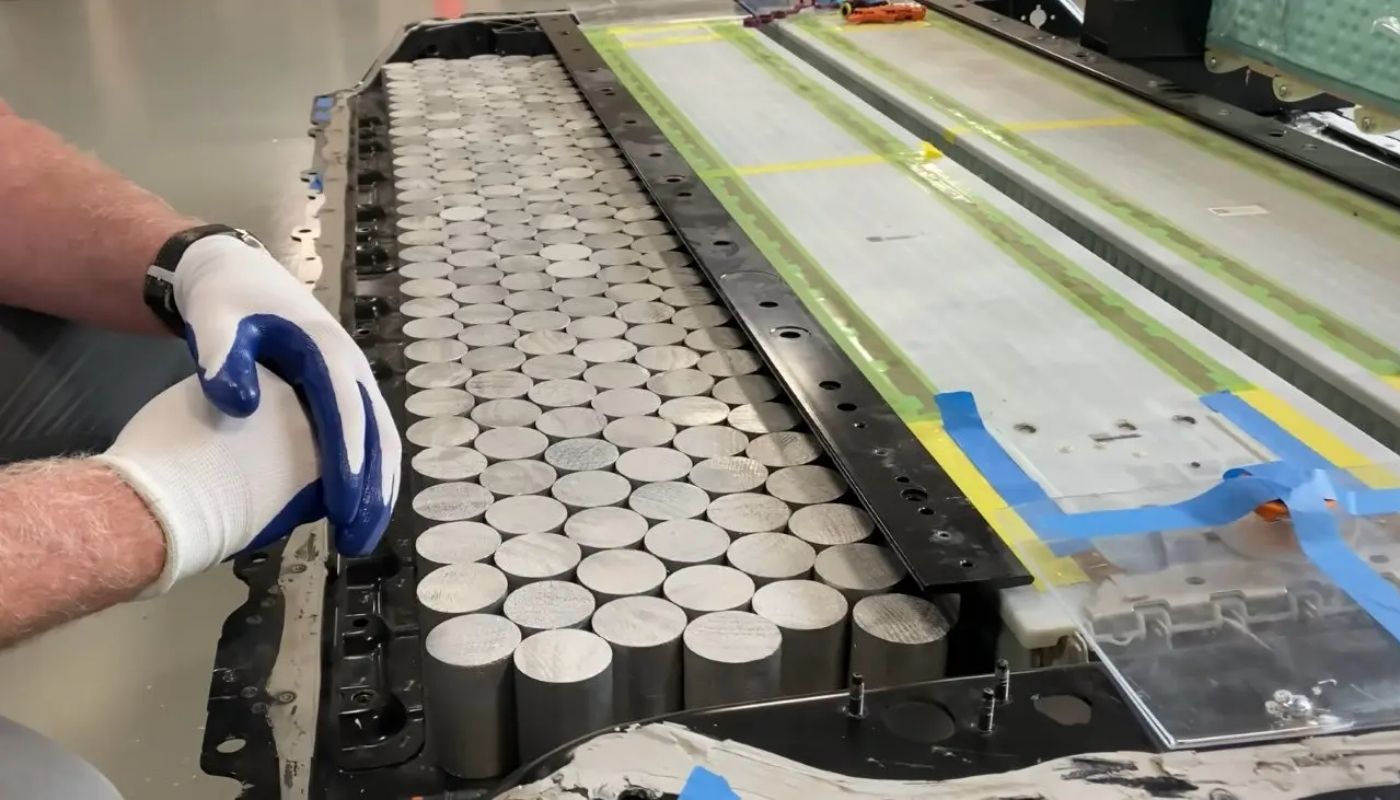
Lithium iron phosphate or LFP is at the heart of new technologies for electric vehicle manufacturers. Now, Tesla has developed a potentially game-changing LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) battery manufacturing process that could revolutionize their battery supply chain.
This could give the company a huge edge over some of its current suppliers and competition. The new process is expected to improve efficiency over existing methods, lower production costs and make battery production more sustainable and efficient in their European and US facilities.

Tesla Patents Low-Cost LFP Battery Manufacturing Process
Patent Number WO2025015194A1 was filed by Tesla last year on 11th July and is published on 16th January 2025. The title of the patent is ACTIVE MATERIAL PARTICLES, PROCESSES THEREOF, AND APPARATUSES USEFUL IN THE MANUFACTURE THEREOF
X user @seti_park gave a brief detail about the new Tesla patent. As per him, Tesla’s new patent WO2025015194A1 modernizes battery active material production by introducing a novel particle size control method. Conventional techniques of manufacturing battery active materials, especially related to LFP, involve many processing steps and expensive tools, such as fine-particle calcination furnaces.
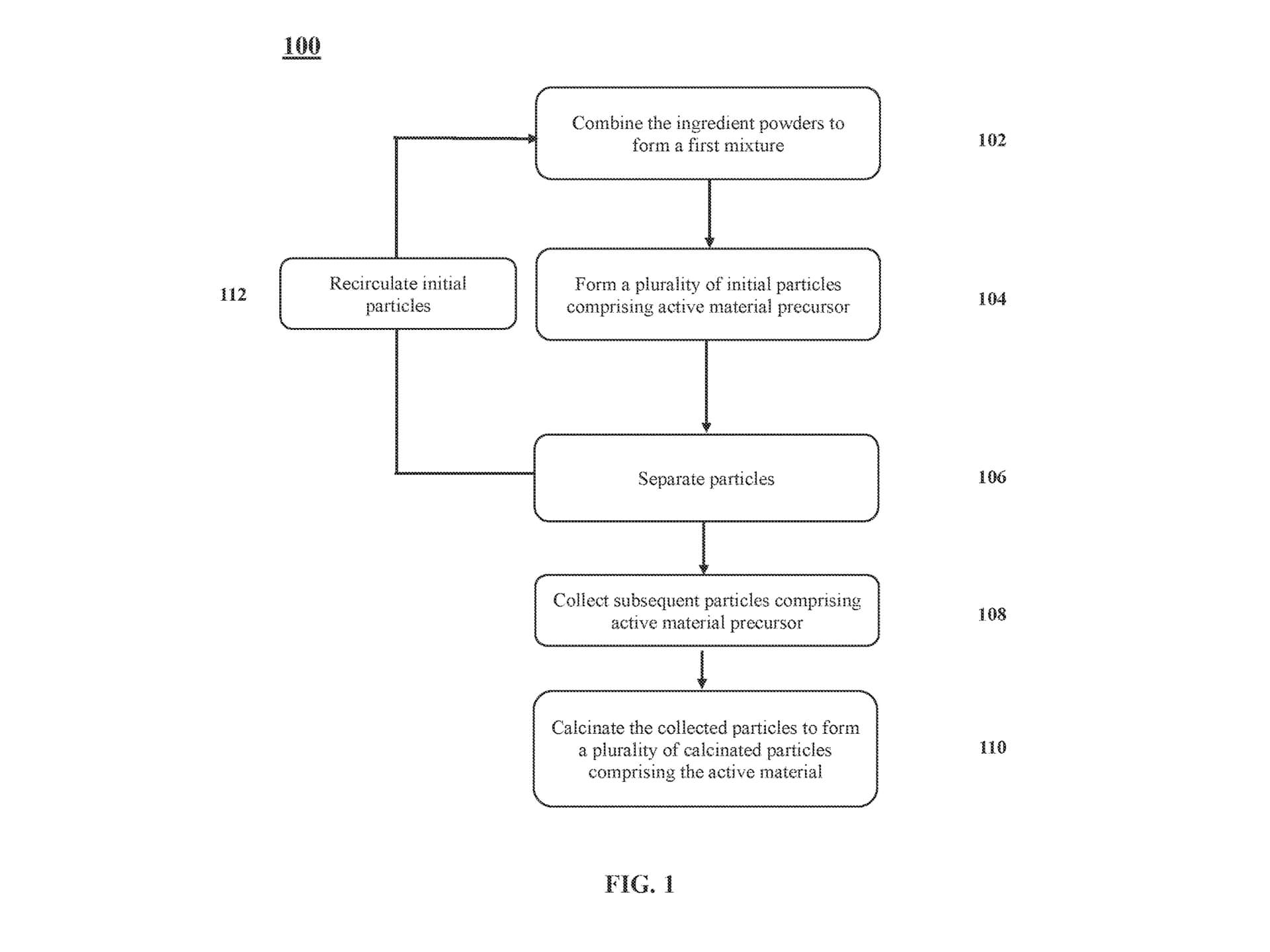
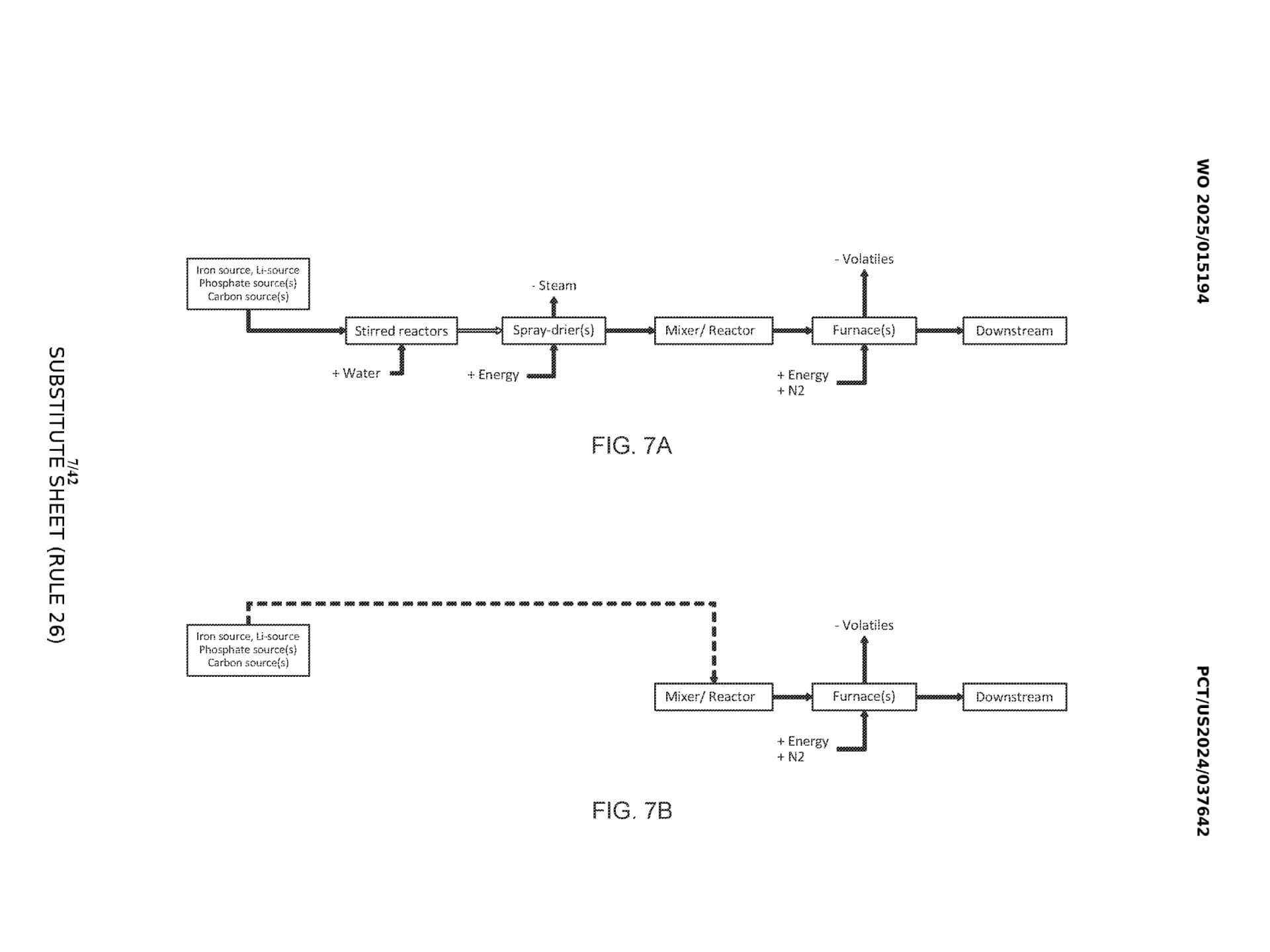
This adds complications to the manufacturing process and has the added effect of raising the production cost while at the same time reducing the ease with which manufacturing can be ramped up. Tesla’s patent resolves these issues by proposing a new particle growth and recirculation system that will make use of conventional furnaces and not give poor material performance.
The focus of the patent can best be defined based on its approach to the particle processing aspect. Rather than processing targeted microparticles which are delicate and need to be recovered and reused, the system takes tiny starting particles and converts them into bigger, subsequent particles in a controlled recirculation manner.
It is convenient for manufacturing while at the same time producing well-ordered crystalline structures with improved characteristics. The process achieves this while significantly reducing manufacturing complexity and cost, marking a substantial advance in battery material production technology.
The Importance of LFP Batteries in EVs
Lithium iron phosphate or LFP batteries have gradually found demand among EV manufacturers because of their long life cycle, safety, and affordability. As contrasted to up-and-coming formats NCA or NMC, LFP batteries have iron and phosphate as the main components, thereby, no the demand for exotic and costly metals such as cobalt and nickel. This not only brings down the price of LFP batteries but also eliminates most of the issues with mining these materials, environmental and ethical.
As mentioned Tesla has been deploying LFP batteries in its vehicles including standard range Model 3 and Model Y. These batteries have a longer life cycle, better thermal characteristics, and give good consistent output. Nevertheless, the biggest consequence has been the fact that they offer lower energy density than NCA and NMC battery types, thus constraining the driving range of electric vehicles.
This smart act of patenting its own LFP production technology will likely have dire consequences on Tesla’s partnerships with battery makers including CATL, LG Energy Solution, and Panasonic. By creating an in-house battery production, Tesla has the opportunity to decrease its dependency on outside suppliers, define its battery supply chain, and exercise more control over the price and quality.
This can be explained by the initiatives that Tesla has been implementing in the past years, collectively known as vertical integration, under which the company tries to direct control over some critical activities. Of course, Tesla has already gained a lot by implementing the vertically integrated model, including the manufacturing of EV motors, self-driving, and software development. Extending LFP battery manufacturing to its portfolio strengthens this model even further.
Although the new patent is positive for Tesla it remains to be proven that they can begin mass production to implement the new process as well as prove that it brings the amount of benefits expected. Battery production is quite a technical process and even minor alterations to the chemistry of the compound or the process parameters can bring about wide variation in the efficiency and performance of the battery.



